IP addresses play an integral role in enabling communication across the vast landscape of the internet. An IP address, standing for Internet Protocol address, serves as a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network, allowing it to be recognized and communicate with other devices on the internet.In the digital age, where connectivity is the cornerstone of our everyday lives,
What is an IP Address?
At its core, an IP address is a numerical label, akin to a physical address in the real world, but for devices connected to a network. It serves as a means of identification and location, allowing devices to send and receive data across the internet.
Types of IP Addresses
There are two primary types of IP addresses:
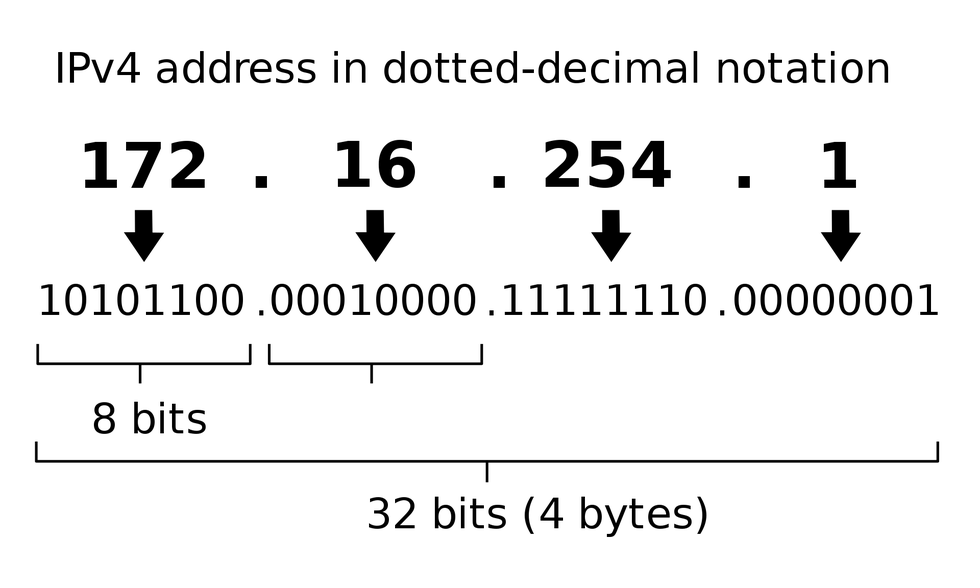
1). IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4): This is the older and more widely used version. An IPv4 address is represented by a series of four numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.1.1. However, due to the increasing number of devices connecting to the internet, the available pool of IPv4 addresses has become limited.
2). IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6): IPv6 was introduced to address the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. It employs a longer addressing system, using a hexadecimal format and separated by colons, like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. IPv6 offers a vastly expanded pool of unique addresses, allowing for the continued growth of internet-connected devices.
How Does an IP Address Work?
When you connect a device to the internet, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns it an IP address. This address acts as the device’s identifier, facilitating communication with other devices or servers on the internet.
Every time you visit a website, send an email, stream a video, or perform any online activity, your device uses its IP address to send and receive data packets to and from the destination. These data packets contain information about the sender’s IP address, the recipient’s IP address, and the content being transmitted.
Purpose and Function
The primary function of an IP address is to enable communication and facilitate the transfer of data between devices. Whether you’re accessing a website, connecting to a server, or engaging in any online activity, your device’s IP address is crucial for routing information to the correct destination and receiving responses.
IP Address and Privacy
IP addresses can also be used to track a device’s approximate location. While they don’t provide exact physical addresses, they can reveal the general geographic location of a device, which raises privacy concerns. To mitigate this, technologies like VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are used to mask or change an IP address, enhancing privacy and security online.
Conclusion
In essence, an IP address is the cornerstone of internet communication, serving as a digital identifier for devices and enabling the seamless transfer of information across networks. As technology evolves and the number of connected devices continues to soar, understanding the fundamentals of IP addresses becomes increasingly vital in navigating the digital landscape.

FAQs about IP address
1. What exactly is an IP address?
Think of an IP address as a digital ID for your gadgets, like a home address but for the internet. It’s a set of numbers assigned to your phone, laptop, or any device connected to the internet. This ID helps them find each other and share information online.
2. Why do I need to care about my IP address?
Your IP address is crucial for doing anything online—whether browsing websites, sending emails, or streaming videos. It’s how your device talks to others on the internet. Knowing your IP address helps you troubleshoot connection issues and can also safeguard your privacy online.
3. Can my IP address reveal personal information?
While it doesn’t spill out your name or exact location, it can give away some general info about where your device is. That’s why some people use tools like VPNs to hide their IP addresses and keep their online activities more private.
4. What’s the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
IPv4 and IPv6 are just different versions of these ID numbers. IPv4, the older version, looks like four sets of numbers (like 192.168.1.1), while IPv6 is longer and looks more complicated (like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). The newer version, IPv6, was created because we’re running out of the older addresses due to the growing number of devices connecting to the internet.
5. Can I change my IP address?
Yes, you can! Sometimes your IP address changes automatically when you restart your router or connect to a different network. But if you want to manually change it for privacy or security reasons, you can use tools like VPNs or proxies to switch to a different IP address.
If you want to know your IP click here
If you want to know about VPN click here
